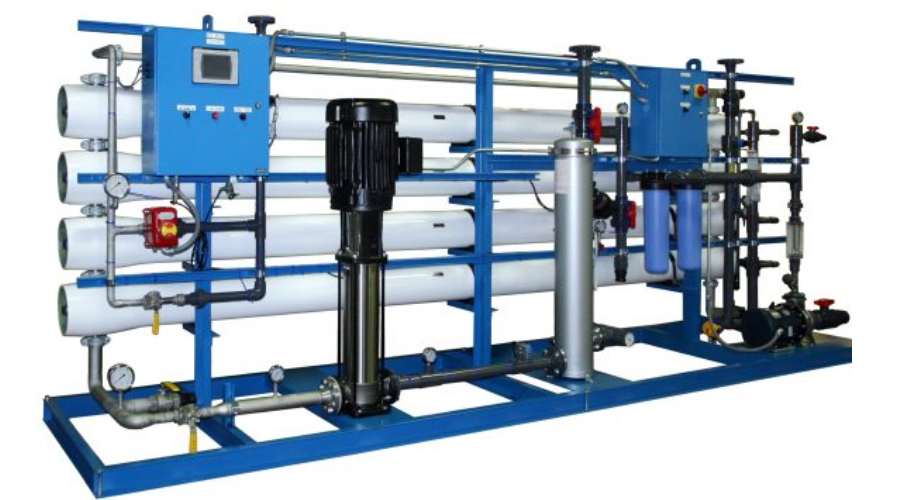
REVERSE OSMOSIS PLANTS
(RO) is a separation process that uses pressure to force a solution through a membrane that retains the solute on one side and allows the pure solvent to pass to the other side. More formally, it is the process of forcing a solvent from a region of high solute concentration through a membrane to a region of low solute concentration by applying a pressure in excess of the osmotic pressure. This is the reverse of the normal osmosis process, which is the natural movement of solvent from an area of low solute concentration, through a membrane, to an area of high solute concentration when no external pressure is applied. The membrane here is semi permeable, meaning it allows the passage of solvent but not of solute.
The membranes used for reverse osmosis have a dense barrier layer in the polymer matrix where most separation occurs. In most cases the membrane is designed to allow only water to pass through this dense layer while preventing the passage of solutes (such as salt ions). This process sthe membrane.In water filter terms, reverse osmosis (or hyper-filtration) is the process of filtering water under pressure through a semi-permeable membrane, allowing water to pass through but rejecting other particles such as bacteria, toxins, salts, and anything bigger than around 150 Daltons The principal uses of reverse osmosis in Minnesota and the Dakotas are for the reduction of high levels of nitrate, sulfate, sodium and total dissolved solids.